By Harvey Ico, backend engineer at Unifa.
Building your own API structure can be chaotic specially if you have a lot of endpoints, and maintaining documentations are troublesome. If you've been a backend engineer for a while now like me, you probably already tried to search "how to organize" your API routes, documentations, etc. And you probably saw GraphQL at some point.
GraphQL was developed internally by Facebook in 2012 before being publicly released in 2015. But what is it actually? Well, to put it simply, GraphQL is a query language for your API. How it works is that you will have a single API endpoint wherein you can pass query or mutation to get your desired outcome. I think what makes it really cool is that you can pass multiple queries or mutations at once. Hence, it became really popular on SPA (Single page application) websites when integrating their API, specially if you are using VueJS, React, etc.
But how do you even build or use it? Don't know where to start? Then you've come at the right place. Here, I'm going to guide you how to build your own GraphQL API using Ruby on Rails.
Installation
For this test app, I'm going to use Rails 7.04 and Ruby 3.1.2 as it is the most recent stable version at the time of this writing. Add this to your Gemfile:
gem 'graphql' group :development do gem 'graphiql-rails' end
Fortunately, there exists a graphql ruby wrapper already. As for graphiql-rails, this will be our IDE tool later to test our queries or mutations.
Initial setup
After installing the gem, you need to run:
rails generate graphql:install
This will generate the following:
harvey.ico/graphql_blog (main ✗) rails generate graphql:install create app/graphql/types create app/graphql/types/.keep create app/graphql/graphql_blog_schema.rb create app/graphql/types/base_object.rb create app/graphql/types/base_argument.rb create app/graphql/types/base_field.rb create app/graphql/types/base_enum.rb create app/graphql/types/base_input_object.rb create app/graphql/types/base_interface.rb create app/graphql/types/base_scalar.rb create app/graphql/types/base_union.rb create app/graphql/types/query_type.rb add_root_type query create app/graphql/mutations create app/graphql/mutations/.keep create app/graphql/mutations/base_mutation.rb create app/graphql/types/mutation_type.rb add_root_type mutation create app/controllers/graphql_controller.rb route post "/graphql", to: "graphql#execute" route graphiql-rails create app/graphql/types/node_type.rb insert app/graphql/types/query_type.rb create app/graphql/types/base_connection.rb create app/graphql/types/base_edge.rb insert app/graphql/types/base_object.rb insert app/graphql/types/base_object.rb insert app/graphql/types/base_union.rb insert app/graphql/types/base_union.rb insert app/graphql/types/base_interface.rb insert app/graphql/types/base_interface.rb insert app/graphql/graphql_blog_schema.rb
Tip (Optional): Please read this first before proceeding. As I will be using this as reference for my classes
Personally, I like to move and rename all the default classes generated from app/graphql/types and app/graphql/mutations to app/graphql/base_types/ folder.
This will make it easier to see which ones are the default base types/mutations and which files were manually created by you.
Additionally:
- Move the
app/graphql/types/query_type.rbtoapp/graphql/query_root.rb - Move the
app/graphql/types/mutation_type.rbtoapp/graphql/mutation_root.rb
And after that, modify app/graphql/*_schema.rb. For example:
class GraphqlBlogSchema < GraphQL::Schema mutation(MutationRoot) query(QueryRoot) end
After making adjustments, this is how your folder should look like:
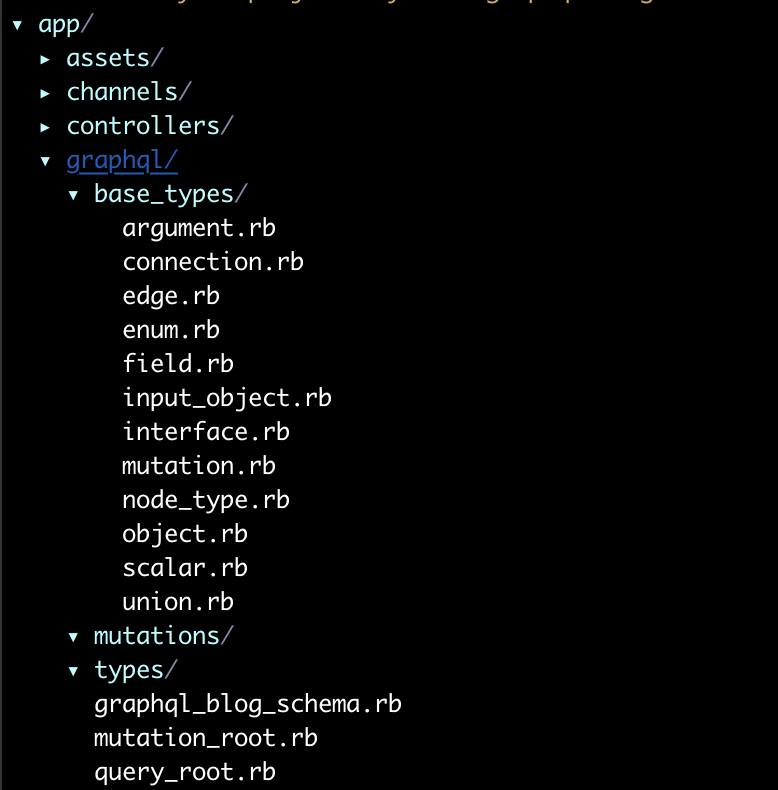
Implementing your first Query
Implementing queries are very straightforward. First you need to create your "Type", then add it to your query_root.rb. For example:
Create a new file app/graphql/types/blog.rb. Then add following:
class Types::Blog < BaseTypes::Object field :id, ID, null: false field :title, String, null: false field :content, String, null: false end
Then inside your app/graphql/query_root.rb. Add this:
class QueryRoot < BaseTypes::Object
include GraphQL::Types::Relay::HasNodeField
field :blogs, [Types::Blog], null: false
def blogs
Blog.order(created_at: :desc)
end
end
and.. Done! Obviously, the above Blog query returns everything. Depending on your use-case, you may need to add arguments or even pagination here.
For testing, run your rails server and open http://localhost:3000/graphiql. Play around with it:
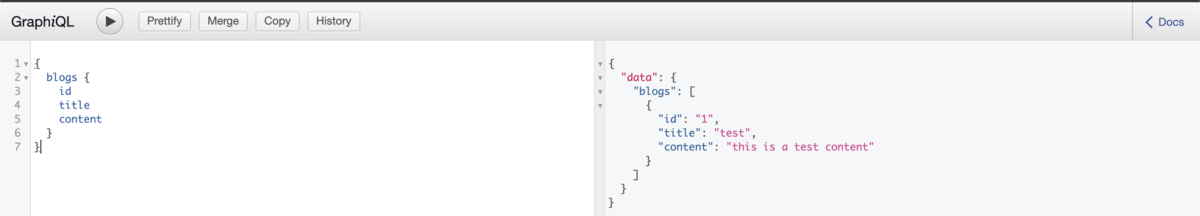
Easy right? But how do we "create or update records"!? The answer for that will be mutation!
Implementing your first Mutation
Implementing mutations are almost the same as the Query. First you need to create your "mutation", then add it to your mutation_root.rb. For example:
Create a new file app/grapqhl/types/error.rb. Then add the following:
class Types::Error < BaseTypes::Object field :field, String, null: false field :messages, [String], null: false end
Create a new file app/graphql/mutations/create_blog.rb. Then add the following:
class Mutations::CreateBlog < BaseTypes::Mutation
description 'Creates a blog record'
argument :title, String, required: true
argument :content, String, required: true
field :blog, Types::Blog, null: true
field :success, String, null: true
field :errors, [Types::Error], null: true
def resolve(params)
blog = Blog.new(params)
if blog.save
{ blog: blog, success: 'Blog created.' }
else
errors = blog.errors.messages.map do |key, messages|
{ field: key, messages: messages }
end
{ errors: errors }
end
end
end
Then inside your app/graphql/mutation_root.rb. Add this:
class MutationRoot < BaseTypes::Object field :create_blog, mutation: Mutations::CreateBlog end
That's it! Doesn't it feel great not having to worry about setting up your routes, controllers, and so on?
For testing, access http://localhost:3000/graphiql and play around it:
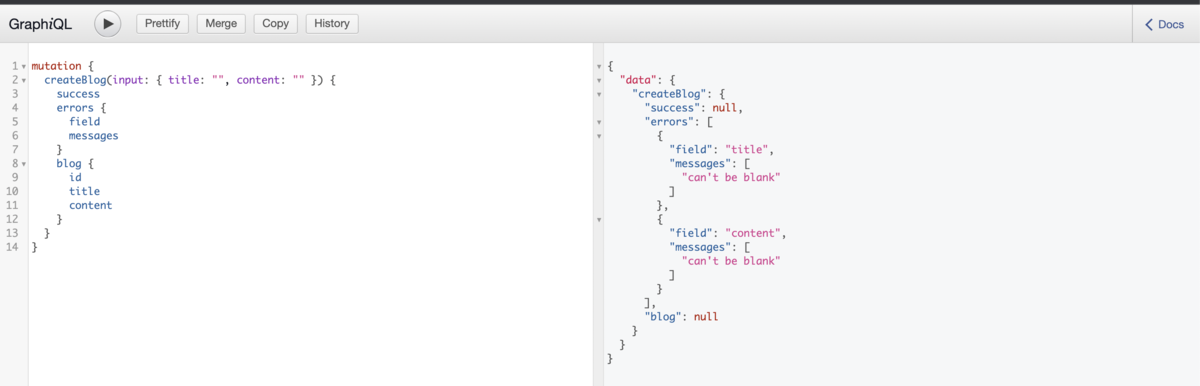
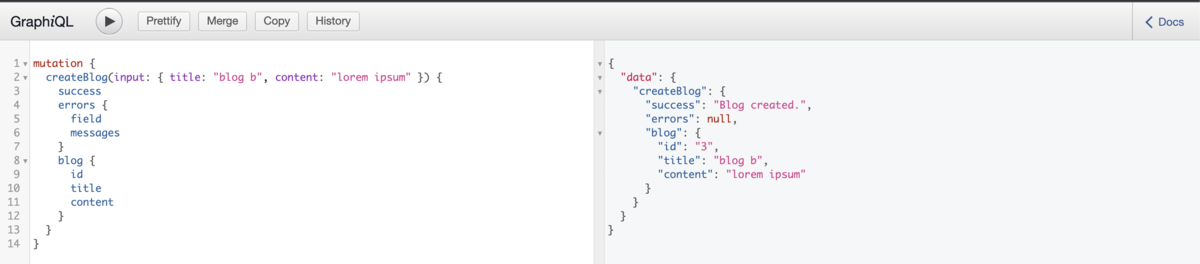
Final thoughts
GraphQL is a very strong API architecture in my opinion. Even just the graphiql can served as documentation when browsing your APIs which is very handy. Obviously, what I covered here were the very basics. If you want to know how to setup "nested queries", or uploading files, etc. That will be your assignment to research
If you are having problems setting up your application, have a look at the github repository that I used on this blog:
If you are wondering what tool to use in order to integrate graphql in your frontend websites. I highly recommend Apollo. For example, you can use vue-apollo on your VueJS app.
And that's it! I hope you had a good read, thanks for reading this far. See ya!
Harvey
Unifa is actively recruiting, please check our website for details: